Advancing Zero-shot Text-to-Speech Intelligibility across
Diverse Domains via Preference Alignment
Abstract
Modern zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) systems, despite using extensive pre-training, often struggle in challenging scenarios such as tongue twisters, repeated words, code-switching, and cross-lingual synthesis, leading to intelligibility issues. This paper proposes to use preference alignment to address these challenges. Our approach leverages a newly proposed Intelligibility Preference Speech Dataset (INTP) and applies Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), along with our designed extensions, for diverse TTS architectures. After INTP alignment, in addition to intelligibility, we observe overall improvements including naturalness, similarity, and audio quality for multiple TTS models across diverse domains. Based on that, we also verify the weak-to-strong generalization ability of INTP for more intelligible models such as CosyVoice 2 and Ints. Moreover, we showcase the potential for further improvements through iterative alignment based on Ints.
INTP: Intelligibility Preference Speech Dataset
We establish a synthetic Intelligibility Preference Speech Dataset (INTP), including about 250K preference pairs (over 2K hours) of diverse domains. The dataset exhibits the following distinctive features:
- Multi-Scenario Coverage: The dataset encompasses various scenarios including regular speech, repeated phrases, code-switching contexts, and cross-lingual synthesis.
- Diverse TTS Model Integration: The dataset leverages three TTS models of different architectures for data generation, including:
-
Diverse Preference Pair Construction: We design three categories of preference pairs,
-
Intra Pair:
Generated through model self-comparison using Best-of-N sampling.
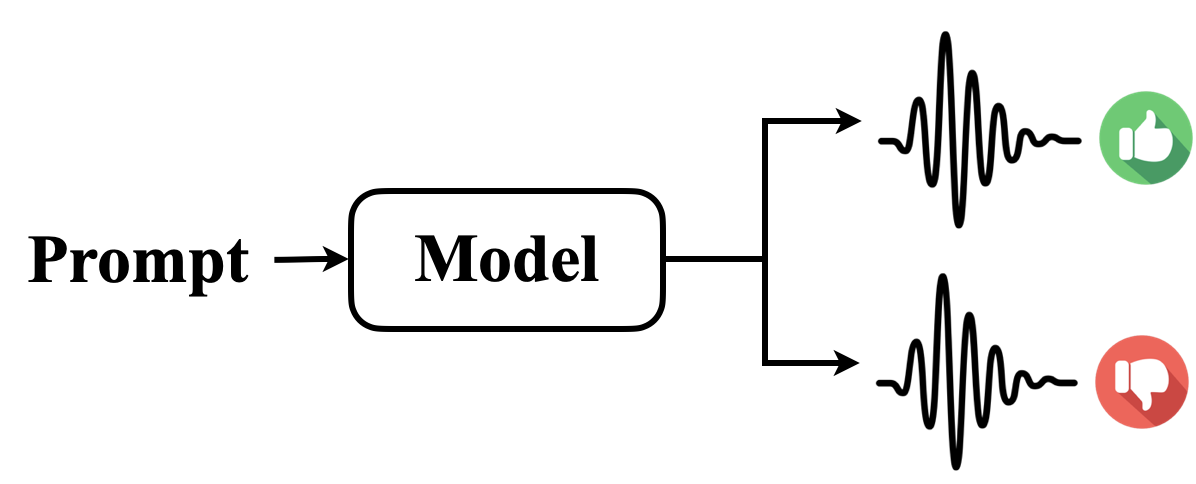
-
Inter Pair:
Created by comparing outputs across different models, enabling the exploitation
of their complementary strengths.
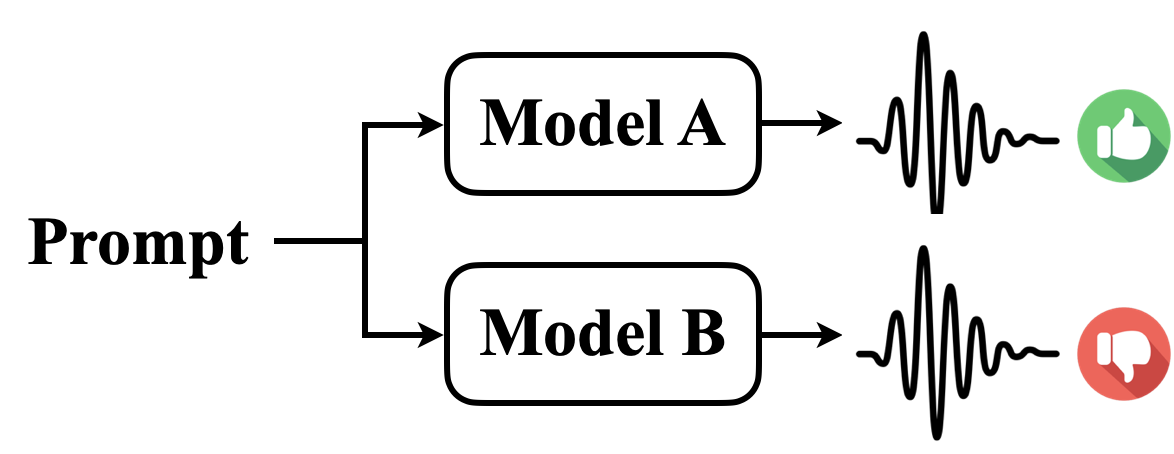
-
Perturbed Pair:
Developed through the integration of human expertise and the advanced capabilities
of LLM (DeepSeek-V3) to generate
human-guided
negative
samples. We design two specific types of text perturbations:
- Pronunciation perturbation: We replace certain characters of the text with easily mispronounceable alternatives.
- Punctuation perturbation: We modify the punctuation, such as commas, to alter pause patterns and prosody in the text.

-
Intra Pair:
Generated through model self-comparison using Best-of-N sampling.
We will present several samples from the INTP dataset as follows.
Monolingual Synthesis
We include two types of monolingual synthesis settings: English (English reference speech with English target text) and Chinese (Chinese reference speech with Chinese target text).
English
Given a same English reference speech, we demonstrate the preference pairs under different target text types:
| Regular | Repeated | Code-Switching | Pronunciation-Perturbed | Punctuation-Perturbed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Speech | {{ egs['en2en'][current_selected_egs['en']]['ars']['regular']['prompt_text'] }} | ||||
| Target Text | {{ egs['en2en'][current_selected_egs['en']]['ars'][col]['target_text'] }} | ||||
| Perturbed Text | - {{ egs['en2en'][current_selected_egs['en']]['ars'][col]['perturbed_text'] }} | ||||
| {{ m(model) }} |
|
||||
Note: You can click the tabs to change the reference speech, and view pairs generated by different models.
Chinese
Given a same Chinese reference speech, we demonstrate the preference pairs under different target text types:
| Regular | Repeated | Code-Switching | Pronunciation-Perturbed | Punctuation-Perturbed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference Speech | {{ egs['zh2zh'][current_selected_egs['zh']]['ars']['regular']['prompt_text'] }} | ||||
| Target Text | {{ egs['zh2zh'][current_selected_egs['zh']]['ars'][col]['target_text'] }} | ||||
| Perturbed Text | - {{ egs['zh2zh'][current_selected_egs['zh']]['ars'][col]['perturbed_text'] }} | ||||
| {{ m(model) }} |
|
||||
Note: You can click the tabs to change the reference speech, and view pairs generated by different models.
Cross-Lingual Synthesis
We include two types of cross-lingual synthesis settings: zh2en (Chinese reference speech with English target text) and en2zh (English reference speech with Chinese target text):
| Example #{{ i }} | |
|---|---|
| Reference Speech | {{ egs[current_selected_egs['set']][i]['ars']['regular']['prompt_text'] }} |
| Target Text | {{ egs[current_selected_egs['set']][i]['ars']['regular']['target_text'] }} |
| {{ m(model) }} |
|
Note: You can click the tabs to change the cross-lingual setting, and view pairs generated by different models.
Results of INTP Alignment
To verify the effectiveness of DPO with INTP for existing TTS models, we conduct alignment experiments with multiple models. First, we evaluate the alignment effectiveness on the three models that participated in INTP construction: ARS, F5-TTS, and MaskGCT:
To investigate INTP's weak-to-strong generalization capability on more powerful base models, we research its alignment effects on CosyVoice 2 (Du et al., 2024), and Ints (Appendix D of our paper). Both models are initialized from textual LLMs (CosyVoice 2: from Qwen-2.5, 0.5B. Ints: from Phi-3.5-mini-instruct, 3.8B) and achieve superior intelligibility performance (Table 4 of our paper). Although CosyVoice 2 and Ints did not participate in INTP construction, we observe that INTP remains effective for them:
{{ expt_m(model) }}
| Domain | Target Text | Reference | {{ expt_m(model) }} | {{ expt_m(model) }} w/ INTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| {{ m(domain) }} | {{ item.target_text }} | {{ item.prompt_text }} |
Note: The INTP dataset does not contain data generated by Ints.
Note: The INTP dataset does not contain data generated by CosyVoice 2.